



suivant: Rotationnal : curl
monter: Multivariate calculus
précédent: Hessian matrix : hessian
Table des matières
Index
Divergence : divergence
divergence takes two arguments : a vector
field of dimension n depending on n real variables.
divergence returns the divergence of F that is the sum
of the derivative of the k-th component with respect
to the k-th variable. For example in dimension n = 3:
divergence([A,B,C],[x,y,z])=
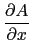
+
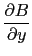
+
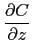
Input :
divergence([x*z,-y^2,2*x^y],[x,y,z])
Output :
z+-2*y
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse