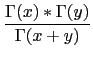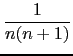



suivant: Derivatives of the DiGamma
monter: Real numbers
précédent: The function : Gamma
Table des matières
Index
The 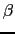 function : Beta
function : Beta
Beta takes as argument two reals a, b.
Beta returns the value of the 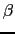 function at
a, b
function at
a, b 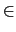
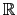 , defined by :
, defined by :
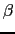
(
x,
y) =
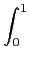 tx-1
tx-1(1 -
t)
y-1 =
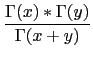
Remarkable values :
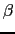
(1, 1) = 1,
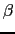
(
n, 1) =
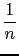
,
(
n, 2) =
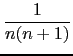
Beta(x,y) is defined for x and y positive reals
(to insure the convergence of the integral) and by
prolongation for x and y if they are not negative integers.
Input :
Beta(5,2)
Output :
1/30
Input :
Beta(x,y)
Output :
Gamma(x)*Gamma(y)/Gamma(x+y)
Input :
Beta(5.1,2.2)
Output :
0.0242053671402
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse