



suivant: Applications
monter: Discrete Fourier Transform
précédent: Discrete Fourier Transform
Table des matières
Index
The Discrete Fourier Transform FN is a bijective transformation
on periodic sequences such that
i.e. :
Inside Xcas the discrete Fourier transform and it's inverse
are denote by fft and ifft:
fft(x)=
FN(x), ifft(x)=
FN-1(x)
Definitions
Let x and y be two periodic sequences of period N.
- The Hadamard product (notation . ) is defined by:
(x . y)k = xkyk
- the convolution product (notation *) is defined by:
(
x*
y)
k =
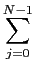 xjyk-j
xjyk-j
Properties :
| N*FN(x . y) |
= |
FN(x)*FN(y) |
|
| FN(x*y) |
= |
FN(x) . FN(y) |
|




suivant: Applications
monter: Discrete Fourier Transform
précédent: Discrete Fourier Transform
Table des matières
Index
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse