



suivant: Equations
monter: Multivariate calculus
précédent: Potential : potential
Table des matières
Index
Conservative flux field : vpotential
vpotential takes two arguments : a vector field
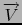 in Rn with respect to n real variables
and the vector of these variable names.
in Rn with respect to n real variables
and the vector of these variable names.
vpotential returns, if it is possible, a vector
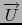 such
that
such
that
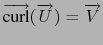 .
When it is possible we say that
.
When it is possible we say that
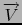 is a conservative flux
field or a solenoidal field.
The general solution is the sum of a particular solution and of the
gradient of an arbitrary function, Xcas returns a particular
solution with zero as first component.
is a conservative flux
field or a solenoidal field.
The general solution is the sum of a particular solution and of the
gradient of an arbitrary function, Xcas returns a particular
solution with zero as first component.
vpotential is the reciprocal function of curl.
Input :
vpotential([2*x*y+3,x^2-4*z,-2*y*z],[x,y,z])
Output :
[0,(-(2*y))*z*x,-x^3/3-(-(4*z))*x+3*y]
In
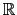 3, a vector field
3, a vector field
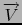 is a rotationnal
if and only if it's
divergence is zero
is a rotationnal
if and only if it's
divergence is zero
(divergence(V,[x,y,z])=0).
In time-independant electro-magnetism,
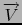 =
=
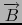 is the magnetic field and
is the magnetic field and
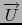 =
=
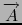 is the potential vector.
is the potential vector.
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse