



suivant: Find the matrix of
monter: Isometries
précédent: Isometries
Table des matières
Index
Recognize an isometry : isom
isom takes as argument the matrix of an linear
application in dimension 2 or 3.
isom returns :
- if the linear application is a direct isometry,
the list of the characteristic elements of this isometry and +1,
- if the linear application is an indirect isometry,
the list of the characteristic elements of this isometry and -1
- if the linear application is not an isometry,
[0].
Input :
isom([[0,0,1],[0,1,0],[1,0,0]])
Output :
[[1,0,-1],-1]
which means that this isometry is a 3-d symmetry with respect to the plane
x - z = 0.
Input :
isom(sqrt(2)/2*[[1,-1],[1,1]])
Output :
[pi/4,1]
Hence, this isometry is a 2-d rotation of angle
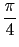 .
.
Input :
isom([[0,0,1],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]])
Output :
[0]
therefore this transformation is not an isometry.
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse