



suivant: Natural splines: spline
monter: Polynomials
précédent: Random list : ranm
Table des matières
Index
Lagrange's polynomial : lagrange interp
lagrange takes as argument two lists of size n (resp a
matrix with two rows and n columns) and the name of a variable
var (by default x).
The first list (resp row) corresponds to the abscissa values xk (k = 1..n),
and the second list (resp row) corresponds to ordinate values yk
(k = 1..n).
lagrange returns a polynomial expression P
with respect to var of degree
n-1, such that
P(xi) = yi.
Input :
lagrange([[1,3],[0,1]])
or :
lagrange([1,3],[0,1])
Output :
(x-1)/2
since
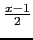 = 0 for x = 1, and
= 0 for x = 1, and
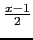 = 1 for x = 3.
= 1 for x = 3.
Input :
lagrange([1,3],[0,1],y)
Output :
(y-1)/2
Warning
f:=lagrange([1,2],[3,4],y) does not return a function
but an expression with respect to y.
To define f as a function, input
f:=unapply(lagrange([1,2],[3,4],x),x)
Avoid f(x):=lagrange([1,2],[3,4],x) since
the Lagrange polynomial would be computed each time f is called
(indeed in a function definition, the second member of the affectation
is not evaluated).
Note also that
g(x):=lagrange([1,2],[3,4]) would not work
since the default argument of lagrange
would be global, hence not the same as the local
variable used for the definition of g.




suivant: Natural splines: spline
monter: Polynomials
précédent: Random list : ranm
Table des matières
Index
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse