



suivant: LU decomposition (for TI
monter: Matrix factorizations
précédent: QR decomposition (for TI
Table des matières
Index
LU decomposition : lu
lu takes as argument a square matrix A of size n (numeric or
symbolic).
lu(A) returns a permutation p of 0..n - 1,
a lower triangular matrix L, with 1 on the diagonal,
and an upper triangular matrix U, such that :
The permutation matrix P is defined from p by :
P[
i,
p(
i)] = 1,
P[
i,
j] = 0 if
j 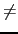 p
p(
i)
In other words, it is the identity matrix where the rows are permuted
according to the permutation p.
The function permu2mat may be used to compute P
(permu2mat(p) returns 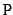 ).
).
Input :
(p,L,U):=lu([[3.,5.],[4.,5.]])
Output :
[1,0],[[1,0],[0.75,1]],[[4,5],[0,1.25]]
Here n = 2, hence :
P[0, p(0)] = P2[0, 1] = 1, P[1, p(1)] = P2[1, 0] = 1, P = [[0, 1],[1, 0]]
Verification :
Input :
permu2mat(p)*A; L*U
Output:
[[4.0,5.0],[3.0,5.0]],[[4.0,5.0],[3.0,5.0]]
Note that the permutation is different for exact input (the choice of
pivot is the simplest instead of the largest in absolute value).
Input :
lu([[1,2],[3,4]])
Output :
[1,0],[[1,0],[3,1]],[[1,2],[0,-2]]
Input :
lu([[1.0,2],[3,4]])
Output :
[1,0],[[1,0],[0.333333333333,1]],[[3,4], [0,0.666666666667]]




suivant: LU decomposition (for TI
monter: Matrix factorizations
précédent: QR decomposition (for TI
Table des matières
Index
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse