



suivant: LCM of two polynomials
monter: Arithmetic and polynomials
précédent: GCD of two polynomials
Table des matières
Index
Choosing the GCD algorithm of two polynomials :
ezgcd heugcd modgcd psrgcd
ezgcd heugcd modgcd psrgcd denotes the gcd
(greatest common divisor) of two univariate or multivariate
polynomials with coefficients
in
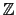 or
or
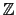 [i] using a specific algorithm :
[i] using a specific algorithm :
- ezgcd ezgcd algorithm,
- heugcd heuristic gcd algorithm,
- modgcd modular algorithm,
- psrgcd sub-resultant algorithm.
Input :
ezgcd(x^2-2*x*y+y^2-1,x-y)
or
heugcd(x^2-2*x*y+y^2-1,x-y)
or
modgcd(x^2-2*x*y+y^2-1,x-y)
or
psrgcd(x^2-2*x*y+y^2-1,x-y)
Output :
1
Input :
ezgcd((x+y-1)*(x+y+1),(x+y+1)^2)
or
heugcd((x+y-1)*(x+y+1),(x+y+1)^2)
or
modgcd((x+y-1)*(x+y+1),(x+y+1)^2)
Output :
x+y+1
Input :
psrgcd((x+y-1)*(x+y+1),(x+y+1)^2)
Output :
-x-y-1
Input :
ezgcd((x+1)^4-y^4,(x+1-y)^2)
Output :
"GCD not successfull Error: Bad Argument Value"
But input :
heugcd((x+1)^4-y^4,(x+1-y)^2)
or
modgcd((x+1)^4-y^4,(x+1-y)^2)
or
psrgcd((x+1)^4-y^4,(x+1-y)^2)
Output :
x-y+1




suivant: LCM of two polynomials
monter: Arithmetic and polynomials
précédent: GCD of two polynomials
Table des matières
Index
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse