



suivant: Factorize a polynomial with
monter: Computing in /p or
précédent: Row reduction to echelon
Table des matières
Index
Construction of a Galois field : GF
GF takes as arguments a prime integer p
and an integer n > 1.
GF returns a Galois field of caracteristic p having pn
elements.
Elements of the field and the field itself
are represented by GF(...) where ... is the following
sequence:
- the caracteristic p (px = 0),
- an irreducible primitive minimal polynomial generating an
ideal I in
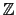 /p
/p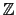 [X], the Galois field being the quotient
of
[X], the Galois field being the quotient
of
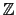 /p
/p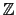 [X] by I,
[X] by I,
- the name of the polynomial variable, by default x,
- a polynomial (a remainder modulo the minimal polynomial)
for an element of the field
(field elements are represented with the additive representation)
or undef for the field itself.
You should give a name to this field (for example G:=GF(p,n)),
in order to build elements of the field from a polynomial in
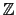 /p
/p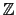 [X], for example G(x
[X], for example G(x^3+x). Note that G(x)
is a generator of the multiplicative group G*.
Input :
G:=GF(2,8)
Output :
GF(2,x^8-x^6-x^4-x^3-x^2-x-1,x,undef)
The field G has 28 = 256 elements and
x generates the multiplicative group
of this field (
{1, x, x2,...x254}).
Input :
G(x^9)
Output :
GF(2,x^8-x^6-x^4-x^3-x^2-x-1,x,x^7+x^5+x^4+x^3+x^2+x)
indeed
x8 = x6 + x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1, hence
x9 = x7 + x5 + x4 + x3 + x2 + x.
Input :
G(x)^255
Output should be the unit, indeed:
GF(2,x^8-x^6-x^4-x^3-x^2-x-1,x,1)
As one can see on these examples, the output contains many times the same
informations that you would prefer no to see
if you work many times with the same field. For this reason,
the definition of a Galois field may have an optionnal argument,
a variable name which will be used thereafter to represent elements
of the field. Since you will also most
likely want to modify the name of the indeterminate, the field
name is grouped with the variable name in a list
passed as third argument to GF.
Note that these two variable names must be quoted.
Example, input :
G:=GF(2,2,['w','G']):; G(w^2)
Output :
Done, G(w+1)
Input :
G(w^3)
Output :
G(1)
Hence, the elements of GF(2,2) are
G(0),G(1),G(w),G(w^2)=G(w+1).
We may also impose the irreductible primitive polynomial that we whish
to use, by putting it as second argument (instead of n),
for example :
G:=GF(2,w^8+w^6+w^3+w^2+1,['w','G'])
If the polynomial is not primitive, Xcas will replace it
automatically by a primitive polynomial, for example :
G:=GF(2,w^8+w^7+w^5+w+1,['w','G'])
Output :
G:=GF(2,w^8-w^6-w^3-w^2-1,['w','G'],undef)




suivant: Factorize a polynomial with
monter: Computing in /p or
précédent: Row reduction to echelon
Table des matières
Index
giac documentation written by Renée De Graeve and Bernard Parisse